CrIS Cloud Emission and Scattering Index (CESI)
July 31, 2017 07:31 AM
by Xioalei Zou
CICS-MD Scientists, in collaboration with NOAA scientists, took an innovative approach for developing a cloud detection algorithm using Cross-Track Infrared Sounder (CrIS) observations. A set of cloud emission and scattering indices (CESI) was developed by properly pairing CrIS shortwave CO2 channels with longwave CO2 channels located at similar altitudes. The global distributions of CESIs derived from CrIS double CO2 bands with weighting functions peaks located at about 321 hPa agreed well with the distributions of ice cloud optical thickness contained in the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) Version 6 data set (see figures below).
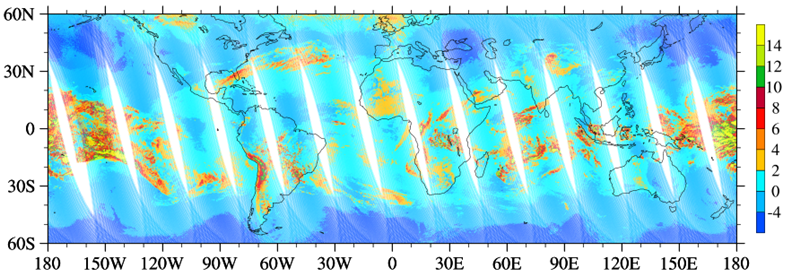
Figure 1: CrIS CESI at 321 hPa
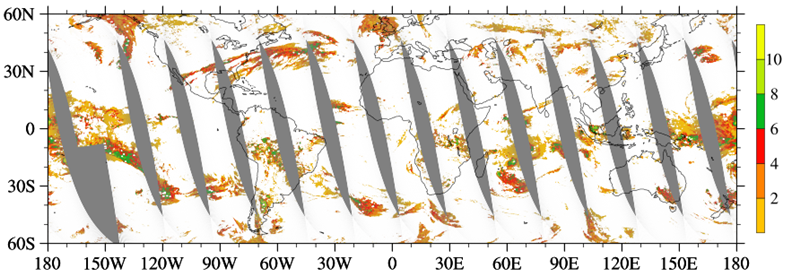
Figure 2: AIRS ice cloud optical depth
The CrIS CESI cloud detection algorithm will be tested and made operationally feasible by determining some threshold values. It will play a significant role in the NOAA CrIS data assimilation system. Lin, L., X. Zou and F. Weng, 2017: Combining CrIS double CO2 bands for detecting clouds located in different vertical layers of the atmosphere. J. Geophy. Res., 122(3), 1811-1827. doi: 10.1002/2016JD025505.
« Back